

The Problem: Every Year, Over 60,000 People Go Blind from Diabetic Retinopathy
LumineticsCore is an Al diagnostic system that autonomously diagnoses patients for diabetic retinopathy (including macular edema)


LumineticsCore is an Al diagnostic system that autonomously diagnoses patients for diabetic retinopathy (including macular edema)




LumineticsCore is for adults (22 years of age or older) diagnosed with diabetes who have not been previously diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy and are not currently under the care of an eye care specialist. LumineticsCore is installed at point-of-care locations to increase patient access and convenience.
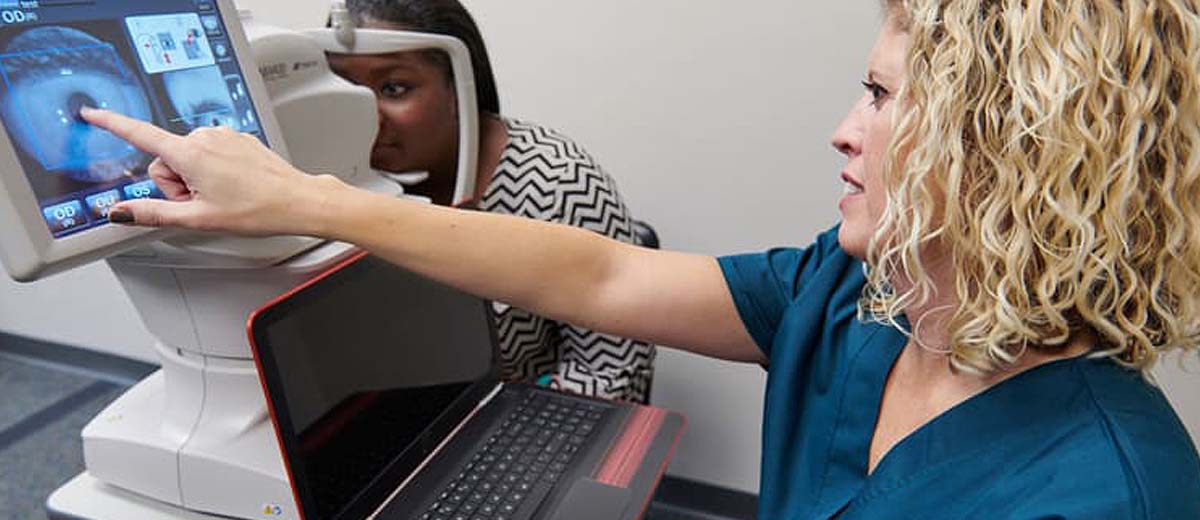

LumineticsCore was validated against patient outcomes using a surrogate outcome standard to keep patient safety the main priority. In the pivotal clinical trial, LumineticsCore referred 100% of patients with at least moderate diabetic retinopathy and more than 96% of patients with diabetic macular edema.
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that affects the eyes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, which can lead to vision problems and even blindness if left untreated.
Diabetic retinopathy is a progressive disease that can affect those with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, causing them to leak or become blocked, which in turn can lead to the growth of abnormal blood vessels.
These new vessels are fragile and can leak blood into the vitreous, the clear gel-like substance that fills the inside of the eye, causing vision loss. Managing blood sugar levels and regular eye exams are essential for preventing or delaying the progression of diabetic retinopathy.

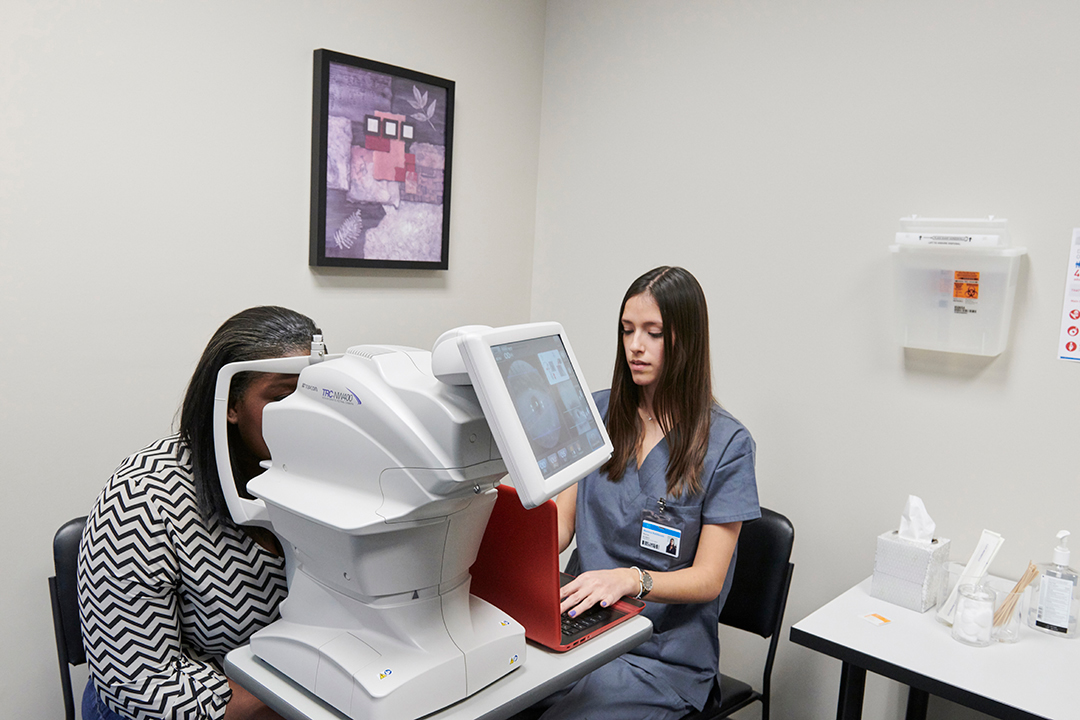
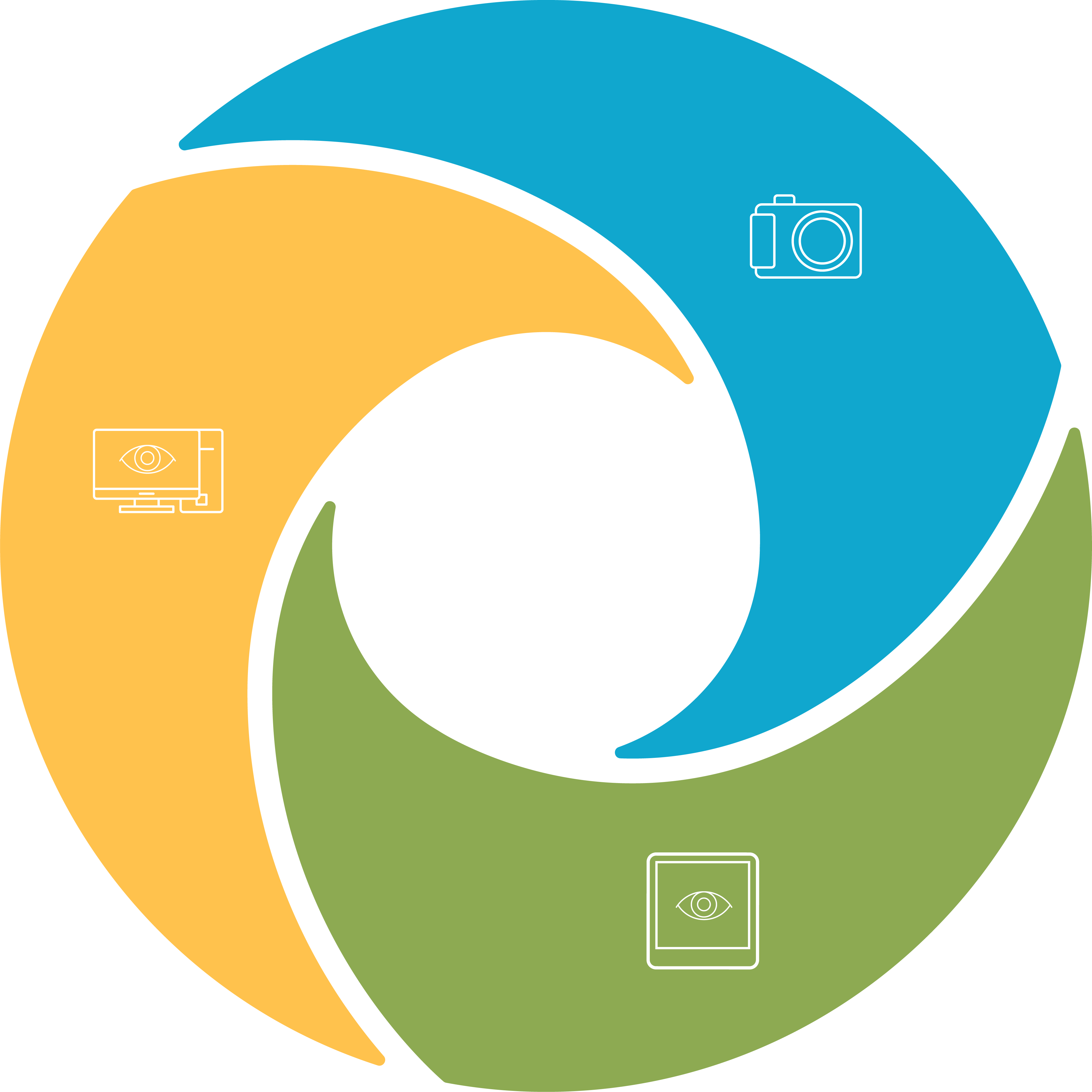
LumineticsCore works by using an artificial intelligence algorithm to analyze images of the retina taken with a retinal camera. The system is designed to detect diabetic retinopathy, a complication of diabetes that affects the eyes and can lead to blindness if left untreated.
During the LumineticsCore scan, your retina will be photographed using a retinal camera. The image is then uploaded to the LumineticsCore software, which uses an AI algorithm to analyze the image and detect signs of diabetic retinopathy.
The algorithm looks for specific changes in the retina, such as the presence of microaneurysms, hemorrhages, or exudates. The algorithm will then determine whether you may have diabetic retinopathy or not based on the severity of these changes.
If the algorithm detects signs of diabetic retinopathy, the system will generate a report that includes the diagnosis and recommendations for further treatment. LumineticsCore is designed to be a fully autonomous system, meaning that it does not require a specialist to interpret the images or make a diagnosis.
This makes the system faster and more efficient than traditional methods of detecting diabetic retinopathy.

No diabetic retinopathy detected: Retest in 12 Months
Diabetic retinopathy detected: Refer to an eye care professional
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that affects the eyes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, which can lead to vision problems and even blindness if left untreated.
Diabetic retinopathy is a progressive disease that can affect those with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, causing them to leak or become blocked, which in turn can lead to the growth of abnormal blood vessels.
These new vessels are fragile and can leak blood into the vitreous, the clear gel-like substance that fills the inside of the eye, causing vision loss. Managing blood sugar levels and regular eye exams are essential for preventing or delaying the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
